출처 : https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/49189
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
문제
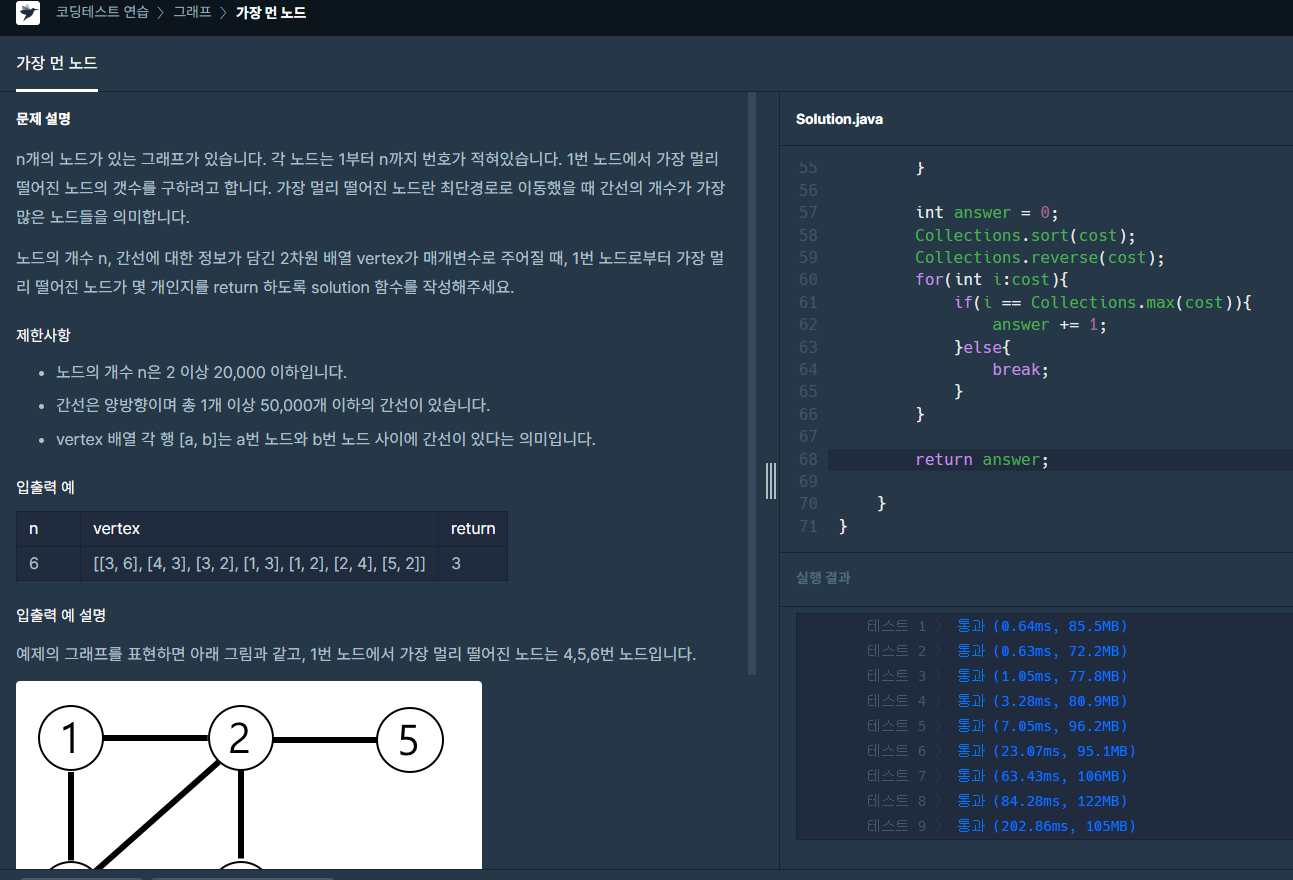
문제 해설
양방향 간선으로 연결된 그래프가 주어진다. 1번 노드에서 가장 멀리 떨어진(가장 먼 거리의) 노드가 모두 몇 개인지 반환하면 된다.
문제 풀이
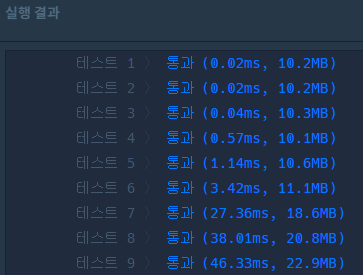
* 여러 방법이 있겠지만 다익스트라 알고리즘을 이용해서 풀었다. 그런데 시간은 인접행렬을 이용하는 방법이 가장 빠르더라.
우선 이 방법은 아래 포스트에서 이용했던 다익스트라 알고리즘을 조금 변형하여 풀었다.
https://chois95.tistory.com/41
[Programmers] 배달_Java
문제 문제 해설 특정 거리로 서로 연결된 graph가 주어진다. graph의 1번 노드에서 다른 노드까지의 거리가 K 이하인 마을의 개수를 반환하면 된다. 문제 풀이 처음에 단순히 dfs로 풀려고 하였으나,
chois95.tistory.com
모두 위 알고리즘과 동일하나, 간선/노드의 개수가 10배 이상으로 많아서 효율을 더욱 증가시켜야 통과할 수 있다. 이를 위한 방법은 두가지다.
(1) 기존 list로 되어있는 graph를 dictionary(hash)로 변환하기
- 다익스트라 수행시 graph를 반복해서 참조하는데, 이를 dictionary로 만들어서 수행시간을 월등히 줄일 수 있다.
(2) 비용 list를 queue로 구현하기
- 다익스트라 수행시, 비용 list를 탐색하면서 방문하지 않은 최소비용값을 반복적으로 탐색해야 한다. 이를 queue를 이용하면, O(N)의 탐색 없이 peek값을 뽑음으로서 O(1)로 시간을 단축시킬 수 있다.
* 코드
- Java Dijkstra algorithm
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Solution {
public int solution(int n, int[][] edge) {
ArrayList<Boolean> checked = new ArrayList(Collections.nCopies(n, false));
Queue<ArrayList<Integer>> costQueue = new LinkedList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
ArrayList<Integer> cost = new ArrayList(Collections.nCopies(n, n + 1));
ArrayList<Integer> now = new ArrayList<Integer>();
cost.set(0, 0);
costQueue.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(0, 0)));
int loc;
int valNow;
int newKey;
ArrayList<Integer> newValue = new ArrayList<Integer>();
HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Integer>>();
for(int i = 0; i < edge.length; i ++){
newKey = edge[i][0];
newValue = graph.getOrDefault(newKey, new ArrayList<Integer>());
newValue.add(edge[i][1]);
graph.put(newKey, newValue);
newValue = graph.getOrDefault(edge[i][1], new ArrayList<Integer>());
newValue.add(newKey);
graph.put(edge[i][1], newValue);
}
while(!costQueue.isEmpty()){
now = costQueue.peek();
loc = now.get(0);
valNow = now.get(1);
costQueue.remove();
if(checked.get(loc) == true){
continue;
}
checked.set(loc, true);
for(int i:graph.get(loc + 1)){
if(checked.get(i - 1) == false){
cost.set(i - 1, Math.min(cost.get(i - 1), valNow + 1));
costQueue.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(i - 1, cost.get(i - 1))));
}
}
}
int answer = 0;
Collections.sort(cost);
Collections.reverse(cost);
for(int i:cost){
if(i == Collections.max(cost)){
answer += 1;
}else{
break;
}
}
return answer;
}
}
- python으로 구현한 Dijkstra algorithm
import heapq
def solution(n, node):
checked = [False for _ in range(n)]
cost = [n + 1 for _ in range(n)]
cost_queue = []
graph = {}
for i in range(len(node)):
new_key = node[i][0]
new_value = node[i][1]
updated_value = graph.get(new_key) or []
updated_value.append(new_value)
graph[new_key] = updated_value
updated_value = graph.get(new_value) or []
updated_value.append(new_key)
graph[new_value] = updated_value
cost[0] = 0
heapq.heappush(cost_queue, [0, 0])
while cost_queue:
val_now, loc = heapq.heappop(cost_queue)
if checked[loc] == True:
continue
checked[loc] = True
for i in graph[loc + 1]:
if checked[i - 1] == False:
cost[i - 1] = min(cost[i - 1], val_now + 1)
heapq.heappush(cost_queue, [cost[i - 1], i - 1])
answer = 0
cost.sort(reverse=True)
for c in cost:
if c == max(cost):
answer += 1
else:
break
return answer
* 아래는 python으로 구현한 인접행렬을 이용한 방법이다. 다익스트라보다 3배 빠르며, bfs를 이용한 것이다.
graph를 deque를 이용해 bfs탐색을 진행하며 루트에서 멀어질 때마다 count ++를 하여, 다음에 방문할 노드의 거리를 갱신시켜주는 방식이다.
이 문제는 최소경로를 구하는 문제가 아니기에, 다익스트라보다 이렇게 bfs를 이용한 탐색이 좀더 적절한 문제인 것 같다.
- 인접행렬을 이용한 방법
from collections import deque
def bfs(start, visited, graph):
count = 0
queue = deque([[start, count]])
while queue:
v = queue.popleft()
target = v[0]
count = v[1]
if visited[target] == -1:
visited[target] = count
count += 1
for e in graph[target]:
if visited[e] == -1:
queue.append([e, count])
def solution(n, node):
answer = 0
visited = []
for i in range(len(node)):
visited.append(-1)
adj = [[] for _ in range(n + 1)]
for e in node:
x = e[0]
y = e[1]
adj[x].append(y)
adj[y].append(x)
bfs(1, visited, adj)
visited.sort(reverse=True)
max_visited = max(visited)
for value in visited:
if value == max_visited:
answer += 1
else:
break
return answer'💡코딩테스트 > HARD' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Programmers]섬 연결하기_Python (0) | 2022.08.16 |
|---|---|
| [Programmers]기지국 설치_Python (0) | 2022.08.08 |
| [Programmers] 배달_Java (0) | 2022.08.01 |
| [Programmers] N으로 표현_Java (0) | 2022.07.19 |
| [Programmers] 소수 찾기_Java (0) | 2022.07.01 |